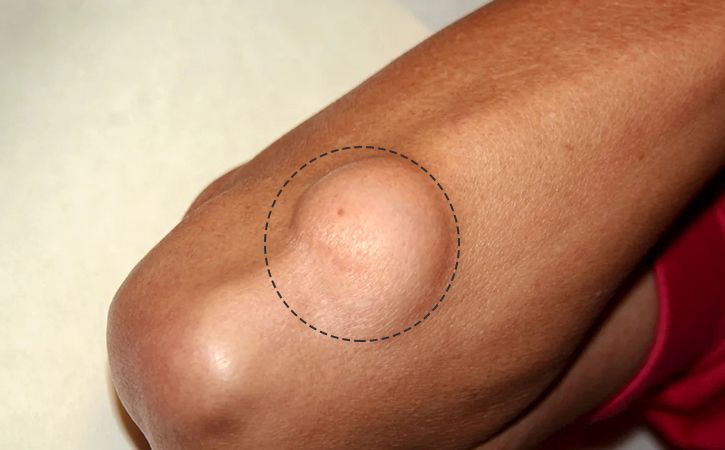
Lipoma is a common benign tumour that typically appears as a soft, rubbery lump under the skin. The article provides details about Lipoma 101 – discussing its causes and treatment options and looking into some of the frequently asked questions.
What is a Lipoma?
The fatty tissue growth that occurs between the skin and the muscle layer is called Lipoma. Lipomas are usually harmless and do not require treatment. However, they can be removed surgically if they cause pain or discomfort.
What Causes Lipomas?
Most lipomas are benign, meaning they are not cancerous. However, there are some rare cases where lipomas can become cancerous. The cause of lipomas is unknown, but there are some theories as to what may contribute to their formation.
One theory is that an overgrowth of fat cells causes them. Another theory is that they are caused by a build-up of toxins in the body or by an imbalance in the body’s hormone levels. Lipomas can develop anywhere on the body, but they are most commonly found on the neck, shoulders, back, and arms.
Treatment options for lipomas include surgery, cryotherapy (freezing), and laser therapy. Surgery is typically only recommended if the Lipoma is causing pain or is located in a visible area. Cryotherapy and laser therapy are less invasive and may be recommended if the Lipoma is small.
Symptoms of Lipomas
Most lipomas are small, measuring less than an inch in diameter. They tend to be soft and rubbery to the touch and usually aren’t painful. You may have more than one Lipoma, which can grow on any body part, including deep within your tissues.
Lipomas grow slowly over time and don’t usually cause any problems unless they press on nerves or blood vessels, which can cause pain or numbness. They can also interfere with organ function if they grow inside the chest or abdomen.
Most people don’t need treatment for their lipomas because they aren’t cancerous and don’t pose any health risks. However, consider treatment if your Lipoma is causing pain or affecting your quality of life in some way. Treatment options include:
- Surgical removal: This is the most common form of treatment for lipomas that are causing problems. An incision is made over the area, removing the tumour and a margin of healthy tissue around it. It helps ensure that all of the cancerous cells are removed.
- Liposuction: This involves using a needle to suction out the fat cells from the Lipoma. It’s generally used for smaller tumours close to the skin’s surface.
- Steroid injections: These injections can help reduce the size of the tumour and relieve pain or discomfort caused by pressure on nearby
How are Lipomas Diagnosed?
There are a few ways that lipomas can be diagnosed. Your doctor will likely start by doing a physical examination and asking about your medical history. They may also order one or more imaging tests, such as an MRI, to get a better look at the tumour.
Once your doctor has diagnosed you with a lipoma, they will work with you to develop a treatment plan. It may involve surgery to remove the tumour, radiation therapy, or other treatments.
Treatment Options for Lipomas
If you have been diagnosed with a lipoma, a few treatment options are available. Lipomas are typically benign (non-cancerous) tumours made up of fat cells. They are slow-growing and usually painless but can cause cosmetic concerns or become large enough to interfere with movement or cause pain.
The most common treatment for lipomas is surgical removal. It can be done through traditional surgery, in which the Lipoma is removed through an incision in the skin, or via minimally invasive surgery, in which the tumour is removed through small incisions using a needle or other instruments.
If Lipoma is small and not causing any problems, your doctor may recommend simply monitoring it rather than removing it.
In rare cases, lipomas can be cancerous. If your doctor suspects that your Lipoma may be cancerous, they will likely recommend a biopsy or removal of the tumour for further testing.
If you have been diagnosed with a lipoma, talk to your doctor about your treatment options and what is right for you.
FAQs about Lipomas
The growth of fatty cells in a thin, fibrous capsule is called Lipoma. They are commonly found just below the skin on the neck, shoulders, back, or trunk but can occur anywhere on the body. Lipomas are usually harmless and do not require treatment.
However, if a lipoma is large or growing, it may cause pain or other problems. In these cases, treatment options include surgery to remove the Lipoma or medication to shrink it.
Look at some frequently asked questions about lipomas:
1. What causes lipomas?
It is unknown what Lipoma’s actual cause is, but they tend to run in families. Obesity and diabetes may also be risk factors.
2. Are lipomas cancerous?
No, lipomas are not cancerous. They are benign (non-cancerous) tumours. However, very rare types of lipomas can be cancerous. If you have any concerns about growth in your body, please see a doctor for an evaluation.
3. How do doctors diagnose lipomas?
Lipomas are usually diagnosed by physical examination. Your doctor will feel the growth to determine if it is soft and movable, like fat under the skin. Sometimes imaging tests such as an ultrasound or MRI are needed to confirm the diagnosis. A biopsy (removal and examination of a small piece of tissue) is rarely necessary.
Conclusion
Lipomas are relatively common, benign growths that can occur anywhere in the body. They’re usually slow-growing and painless, although they can be uncomfortable if they grow too large or press against a nerve.
It is important to consult your doctor if you have any concerns about lipomas, as they can sometimes signal underlying health issues. With accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment options, it’s possible to manage lipoma symptoms and reduce their size so that you can enjoy life with little disruption from these benign growths.